Mastering WordPress Gutenberg (Block Editor): A Beginner Guide (Tutorial + Pro Tips)
WordPress is popular because it gives you control over your content. But that experience gets better with the Gutenberg Block Editor.
Gutenberg makes it easier to create and manage content. You work with blocks instead of shortcodes or custom code. Each block handles one task, like text, images, buttons, or forms.
You can edit everything using visual settings. No coding needed. You see changes as you make them.
That’s why Gutenberg works well for day-to-day content tasks. You can build pages faster and keep full control.
If you’re new to Gutenberg, this guide will help you get started. If you already use it, you’ll still find useful tips.
We’ll walk through the basics first. Then we’ll cover helpful best practices. We’ll also look at common issues and how to fix them.
By the end, you’ll know how to use the Gutenberg editor with confidence.
TL;DR – What You’ll Learn in This Guide
- What the Gutenberg Block Editor is and how it works
- Step-by-step tutorial to create pages using Gutenberg
- Best practices for using and organizing content blocks
- Tips for embedding multimedia and improving SEO
- Pros and cons of using Gutenberg vs Classic Editor
- Common issues and how to troubleshoot them
What is the WordPress block editor, and how does it work?
The WordPress Block Editor, also known as Gutenberg, is a visual content editor that allows users to build pages and posts using modular content blocks. Each block, such as a paragraph, image, or video, can be independently customized, moved, and styled.
Reference: According to the Gutenberg Developer Handbook , blocks are the basic units of content used to build WordPress pages visually.
This block-based approach makes content creation more flexible and user-friendly, especially for beginners, and removes the need for writing custom HTML or shortcodes.
Plus, it replaces code-heavy editing with a clean, drag-and-drop interface, making it easier to build dynamic layouts without technical skills.
Key features and benefits of using Gutenberg
- Block-based layout: Every section of your content is treated as a block, which can be managed and styled independently.
- Full-site editing capabilities:
- Reusable blocks: You can save commonly used blocks and reuse them across different posts or pages to maintain consistency.
- Drag-and-drop interface: Rearrange blocks easily by dragging them into place, allowing full layout control without code.
- Rich media integration: Embed videos, images, galleries, and audio files directly within content blocks.
As noted in the Make WordPress Core blog, Gutenberg is the future of WordPress editing, with continuous improvements added in every core update.
A step-by-step guide on using blocks to build WordPress pages and posts
To use the Gutenberg editor, go to your WordPress dashboard. When you create a new post or page, the Gutenberg editor will open automatically.
Each part of your content—like text, images, or videos—is added as a separate block. You can move, edit, and style each block on its own. This gives you more control over how your page looks.
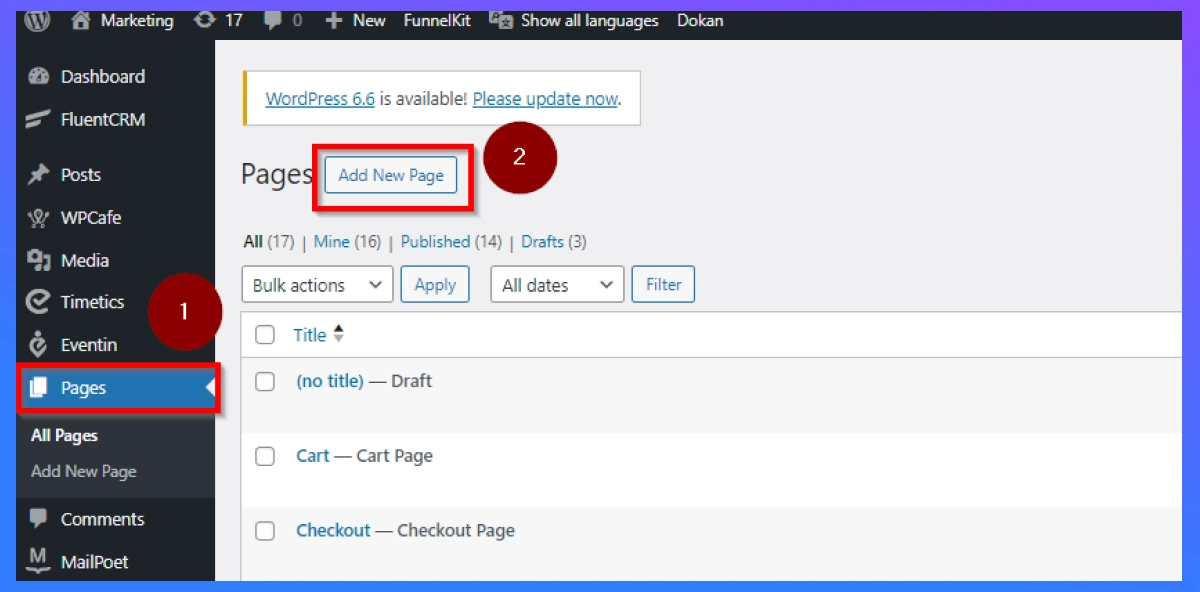
Step 1: Create a new page
Log in to Your WordPress Dashboard: Access your WordPress website’s dashboard by entering your login credentials > Hover over the “Pages” option in the left-hand sidebar > Click on “Add New” to initiate the page creation process.
You can also use the Gutenberg block editor to manage your blog content similarly.
Now, enter a page title: At the top of the page, you’ll find a title field. Type in a descriptive title for your new page. This title will be visible to visitors.

Start building with blocks: The Gutenberg editor presents a clean interface with a “+ Add Block” button. Click this button to access a wide range of block options.
Step 2: Navigate to the basic layout

- Top Toolbar: Contains options for saving, publishing, and undoing changes.
- Sidebar: Contains settings for individual blocks and documents.
- Content Area: Where you add and edit content using blocks.
What types of blocks are available in Gutenberg?

- Paragraph Block: For adding text content.
- Heading Block: For adding headings and subheadings.
- Image Block: For inserting images.
- Gallery: To create image galleries.
- List Block: For creating ordered and unordered lists.
- Button: To add clickable buttons.
- Currently, there are over 90 Guten blocks available.
Step 3: Arrange and customize blocks

Each block has a toolbar that appears when you click on it. This toolbar offers options like:
- Adding, duplicating, or deleting blocks.
- Changing block alignment (left, center, right, wide).
- Accessing block-specific settings.
Drag and drop blocks to rearrange their order. Click on individual blocks to access specific settings and customization options.
Step 4: Preview and publish your page

- As you build your page, you can preview its appearance by clicking the “Preview” button in the top right corner.
- Once you’re satisfied with your page, click the “Publish” button.
- Alternatively, you can save a draft for later editing by clicking “Save Draft”.

Website Frontend View
Gutenberg is evolving fast, and many changes appear at the project level first. Reviewing real Gutenberg updates helps you understand how blocks, editor behavior, and future features take shape before they reach WordPress core.
Get a FULL SITE EDITING experience with the GutenbergWhat are the best practices for organizing content in Gutenberg?
Let’s check out some of the best practices that you should know and implement right away for instant outcomes:
1. Use headings to improve readability and SEO
- Why use headings: Headings help break your content into manageable sections, making it easier for readers to follow. Additionally, they play an important role in SEO by structuring your content.
- How to use them: Use the Heading Block to add headings and subheadings. Choose from H1 to H6, but remember to use them sequentially (e.g., H1 for the main title, H2 for the main sections, and H3 for subsections).
2. Incorporate images, videos, and galleries
- Why use multimedia: Multimedia elements make your content more engaging and visually appealing, which can help retain readers’ attention.
- How to use them: The Gutenberg block editor offers several multimedia blocks, including Image Block, Video Block, and Gallery Block.
- Image block: Upload or select images from your media library. Use the block settings to adjust alignment and size, and add alt text.
- Video block: Embed videos from your media library or external sources like YouTube and Vimeo.
- Gallery block: Create image galleries with customizable layouts and settings.
3. Internal linking for improved navigation and SEO
- Why internal linking: Internal links guide readers to related content on your site, improving their experience and helping search engines crawl your site more effectively.
- How to use it: To create internal links, use the Link Block or add a link to any block. Highlight the text, click the link icon, and paste the URL of the related post or page.
What are the Pros and Cons of the Gutenberg block editor in WordPress

Pros
- User-Friendly: Intuitive drag-and-drop interface suitable for beginners and non-developers.
- Flexibility: Modular block-based approach allows for creative and complex layouts.
- Customization: A wide range of customization options for each block.
- Integrations: Seamless integration with plugins and third-party blocks.
- Innovate: Fully compatible with modern web standards and responsive design.
- More improved performance: It can now take the heavy load of blocks and multimedia.
Cons
- Learning Curve: Users who switch from another WordPress editor may require some time.
- Compatibility: Some older plugins/themes and plugins may not be fully compatible.
WordPress Developer Updates December 2025-26: What Changed and Why It Matters
In December 2025-26, WordPress shared its latest developer update, outlining what shipped in WordPress 6.9 “Gene” and what’s changing behind the scenes.
This update matters even if you don’t write code every day. Core changes affect how blocks work, how plugins behave, and how editors like Gutenberg perform.
What is new in WordPress 6.9 “Gene”?
WordPress 6.9 is the final major release of 2025. It focuses on editor stability, block improvements, and better developer tools.
Here’s what stands out.
New AI experiments for WordPress
WordPress introduced a new AI Experiments plugin. It allows developers to test AI-based features inside WordPress in a safe way.

This is important because:
- AI features are now being tested at the core level
- Future blocks and tools may rely on these experiments
- Plugin developers can prepare early
Progress on experimental Gutenberg blocks
Several experimental blocks continue to evolve, including:
- Breadcrumbs
- Tabs
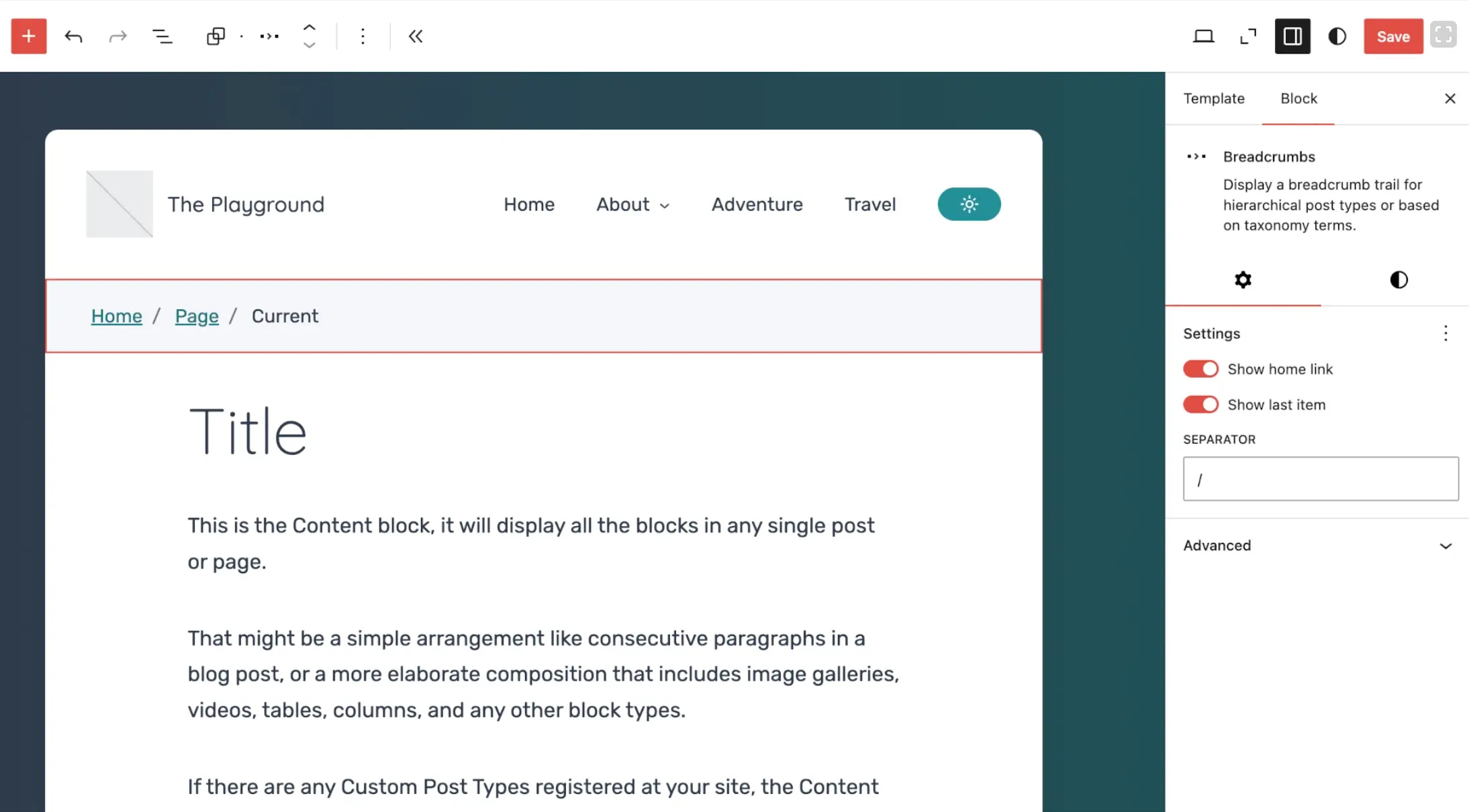
These blocks are not default yet. But they show where the Gutenberg editor is heading next. If you build content-heavy sites, these blocks will matter soon.
Block and editor improvements
The update also includes multiple block-level changes, such as:
- Better handling of border radius values
- Improved Paragraph, HTML, and Accordion blocks
- Cleaner behavior for Term Name and layout settings
These updates make block editing more consistent and predictable.
Developer tools and WordPress playground updates
WordPress Playground received updates to support:
- Faster testing
- Better database handling
- Smoother browser-based development
This helps developers test plugins, blocks, and themes without setting up a full site.
Why this update matters for gutenberg users
Even if you only use Gutenberg to create pages, these updates still affect you.
They lead to:
- More stable blocks
- Better editor performance
- Fewer conflicts with plugins
- A smoother editing experience
If you use Gutenberg regularly, these changes shape how the editor works going forward.
WordPress just published its final developer update for 2025. This covers all the new tools, improvements, and experimental features introduced with WordPress 6.9 “Gene”. If you build with Gutenberg, plugins, or custom blocks, this update has many useful insights.
Read the Full Update on WordPress.orgWhat are the common issues in Gutenberg, and how to fix them?
While using Gutenberg on your WordPress, some issues can hinder your experience. Knowing how to resolve could make your experience easier and better.
Let’s check out:
Issue 1: Block editor not loading or crashing
- Plugin conflicts: To identify the problematic plugin, temporarily deactivate all plugins and then reactivate them one at a time until you find the one.
- Theme compatibility: Try a default WordPress theme to see if it works. If it’s resolved, the theme is likely causing problems.
- WordPress core issues: Ensure WordPress and all its core components are up-to-date.
- Browser compatibility: Try different browsers to see if the issue is browser-specific.
- PHP version: Check if your PHP version is compatible with WordPress and your theme.
Issue 2: Block editor performance issues
- Too many blocks: Reduce the number of blocks on a page for better performance.
- Plugin conflicts: Deactivate performance-heavy plugins temporarily.
- Hosting issues: Contact your hosting provider for performance optimization.
Issue 3: Block alignment and spacing issues
- Theme or Plugin conflicts: Check for compatibility issues with your theme or plugins.
- Custom CSS: Inspect custom CSS for unwanted styling affecting block alignment.
- Block spacing: Use the block spacing controls within the block settings for precise adjustments.
Issue 4: Block editor saving issues
- Browser issues: Try different browsers or clear the browser cache.
- Plugin conflicts: Deactivate plugins to check for interference.
- WordPress core issues: Update WordPress to the latest version.
- Server issues: Contact your hosting provider for troubleshooting.
Issue 5: Block editor display issues (e.g., missing blocks, incorrect rendering)
- Browser compatibility: Try different browsers or update your current one.
- Theme or Plugin conflicts: Deactivate conflicting themes or plugins.
- CSS issues: Check for custom CSS affecting block display.
- JavaScript errors: Inspect the browser console for JavaScript errors.
Issue 6: Additional considerations
- Custom Block development: If you’re developing custom blocks, ensure proper code structure and validation.
- Third-party block plugins: If using third-party block plugins, check for updates and compatibility.
- Performance optimization: Optimize images, minify CSS and JavaScript, and leverage caching for improved block editor performance.
Some common FAQs regarding the Gutenberg blog editor
-
Can I create templates with Gutenberg for multiple pages?
Yes. You can create page layouts using reusable blocks or full block patterns, then save them to reuse across multiple posts or pages.
-
How do I remove extra spacing between blocks in Gutenberg?
Use the block settings panel on the right to adjust padding and margin. You can also fine-tune spacing with the Group block and layout controls.
-
Why do my Gutenberg blocks look different on the front end?
The block editor preview depends on your theme’s styling. To match the front end, use a theme that supports full block styling or editor styles (editor-style.css).
-
Can I lock blocks in Gutenberg to prevent client edits?
Yes. WordPress allows you to lock blocks using block-lock=”true” in the block settings (or via custom code). This is helpful when building client sites.
-
What’s the difference between block patterns and reusable blocks?
Reusable blocks update everywhere when edited. Block patterns are layout presets you insert once and then modify freely without affecting other pages.
-
Does Gutenberg support custom CSS per block?
Yes. Each block includes an “Additional CSS Class” field in the Advanced settings. You can target this class in your custom CSS to style individual blocks.
-
Is it possible to export a page built with Gutenberg?
Yes. You can copy the page content (from the code editor view) or use the native WordPress export tools to export posts/pages with block content.
Gutenberg block tutorial guide summary
The Gutenberg Block Editor makes it easier to create and manage content in WordPress using a simple, visual interface. With blocks, you can build flexible layouts, add rich media, and control the look of your pages without writing code.
In this guide, you learned how to use Gutenberg step by step—from the basics to advanced features. You also discovered best practices, common issues, and how to solve them.
Now it’s your turn. Start experimenting with blocks, improve your content layout, and make the most of what Gutenberg offers. The more you practice, the better your content will look and perform.
More Helpful Resources
- Ensure WordPress Security in Your Website – Learn how to protect your site from threats and vulnerabilities.
- Common WordPress Errors (Part 1) – Fix frequent issues that can break your WordPress site.
- Best WordPress Business Trends 2024 – Discover what’s trending and how to future-proof your WordPress business.
- Website Heatmap Guide – Understand how users interact with your site and improve your layout with real data.



